Living With Achilles Tendinitis Suffering
Overview
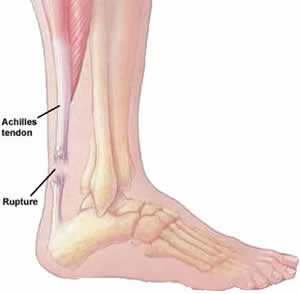 Achilles tendinitis occurs when the band of tissue that connects the calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to the heel bone, the Achilles tendon, becomes inflamed. This condition is a result of overuse from intense exercise, jumping, running, and other activities that strain the tendon and calf muscles.
Achilles tendinitis occurs when the band of tissue that connects the calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to the heel bone, the Achilles tendon, becomes inflamed. This condition is a result of overuse from intense exercise, jumping, running, and other activities that strain the tendon and calf muscles.
Causes
Some of the causes of Achilles tendonitis / tendinosis include. Overuse injury - this occurs when the Achilles tendon is stressed until it develops small tears. Runners seem to be the most susceptible. People who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball, are also at increased risk. Arthritis - Achilles tendonitis can be a part of generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis. In these conditions both tendons can be affected. Foot problems - some people with over pronated feet (Flat Feet) or feet that turn inward while walking are prone to Achilles tendonitis. The flattened arch pulls on calf muscles and keeps the Achilles tendon under tight strain. This constant mechanical stress on the heel and tendon can cause inflammation, pain and swelling of the tendon. Being overweight can make the problem worse. Footwear - wearing shoes with minimal support while walking or running can increase the risk, as can wearing high heels. Overweight and obesity - being overweight places more strain on many parts of the body, including the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Achilles tendonitis include, pain in the back of the heel, difficulty walking, sometimes the pain makes walking impossible, swelling, tenderness and warmth of the Achilles tendon. Achilles tendonitis is graded according to how severe it is, mild - pain in the Achilles tendon during a particular activity (such as running) or shortly after. Moderate - the Achilles tendon may swell. In some cases, a hard lump (nodule) may form in the tendon. Severe - any type of activity that involves weight bearing causes pain of the Achilles tendon. Very occasionally, the Achilles tendon may rupture (tear). When an Achilles tendon ruptures, it is said to feel like a hard whack on the heel.
Diagnosis
Examination of the achilles tendon is inspection for muscle atrophy, swelling, asymmetry, joint effusions and erythema. Atrophy is an important clue to the duration of the tendinopathy and it is often present with chronic conditions. Swelling, asymmetry and erythema in pathologic tendons are often observed in the examination. Joint effusions are uncommon with tendinopathy and suggest the possibility of intra-articular pathology. Range of motion testing, strength and flexibility are often limited on the side of the tendinopathy. Palpation tends to elicit well-localized tenderness that is similar in quality and location to the pain experienced during activity. Physical examinations of the Achilles tendon often reveals palpable nodules and thickening. Anatomic deformities, such as forefoot and heel varus and excessive pes planus or foot pronation, should receive special attention. These anatomic deformities are often associated with this problem. In case extra research is wanted, an echography is the first choice of examination when there is a suspicion of tendinosis. Imaging studies are not necessary to diagnose achilles tendonitis, but may be useful with differential diagnosis. Ultrasound is the imaging modality of first choice as it provides a clear indication of tendon width, changes of water content within the tendon and collagen integrity, as well as bursal swelling. MRI may be indicated if diagnosis is unclear or symptoms are atypical. MRI may show increased signal within the Achilles.
Nonsurgical Treatment
In order to treat achilles tendinitis effectively, it is important to complete a thorough examination of the entire lower extremity. Once the true cause is identified, a comprehensive treatment program can be initiated to reduce inflammation and improve any faulty lower extremity biomechanics. Treatment options may include biomechanical analysis of gait. Splinting/bracing to alleviate the strain on the tendon. Soft tissue mobilization/manual therapy to decrease inflammation and promote healing of the tendon. Strengthening/flexibility and proprioceptive exercises. Home exercise program. Modalities for pain and inflammation (i.e. ultrasound, iontophoresis, electrical stimulation, ice). Methods to alter faulty mechanics (i.e taping, orthotics). Education about lifestyle changes (i.e. proper shoes, activity modification).
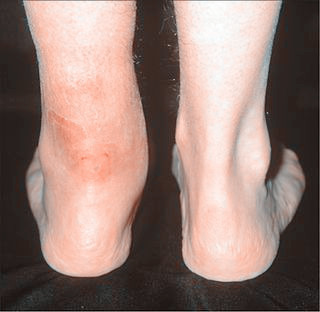
Surgical Treatment
The type of surgery you will have depends on the type of injury you are faced with. The longer you have waited to have surgery will also be a factor that determines what type of surgery is needed. With acute (recent) tearing the separation in your Achilles tendon is likely to be very minimal. If you have an acute tear you may qualify for less invasive surgery (such as a mini-open procedure). Surgeons will always choose a shorter, less invasive procedure if it is possible to do so. Most surgeons know that a less complicated procedure will have less trauma to the tendon and a much quicker rate of recovery after the surgery.
Prevention
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis from recurring after surgical or non-surgical treatment, the foot and ankle surgeon may recommend strengthening and stretching of the calf muscles through daily exercises. Wearing proper shoes for the foot type and activity is also important in preventing recurrence of the condition.
 Achilles tendinitis occurs when the band of tissue that connects the calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to the heel bone, the Achilles tendon, becomes inflamed. This condition is a result of overuse from intense exercise, jumping, running, and other activities that strain the tendon and calf muscles.
Achilles tendinitis occurs when the band of tissue that connects the calf muscles at the back of the lower leg to the heel bone, the Achilles tendon, becomes inflamed. This condition is a result of overuse from intense exercise, jumping, running, and other activities that strain the tendon and calf muscles.
Causes
Some of the causes of Achilles tendonitis / tendinosis include. Overuse injury - this occurs when the Achilles tendon is stressed until it develops small tears. Runners seem to be the most susceptible. People who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball, are also at increased risk. Arthritis - Achilles tendonitis can be a part of generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis. In these conditions both tendons can be affected. Foot problems - some people with over pronated feet (Flat Feet) or feet that turn inward while walking are prone to Achilles tendonitis. The flattened arch pulls on calf muscles and keeps the Achilles tendon under tight strain. This constant mechanical stress on the heel and tendon can cause inflammation, pain and swelling of the tendon. Being overweight can make the problem worse. Footwear - wearing shoes with minimal support while walking or running can increase the risk, as can wearing high heels. Overweight and obesity - being overweight places more strain on many parts of the body, including the Achilles tendon.
Symptoms
Symptoms of Achilles tendonitis include, pain in the back of the heel, difficulty walking, sometimes the pain makes walking impossible, swelling, tenderness and warmth of the Achilles tendon. Achilles tendonitis is graded according to how severe it is, mild - pain in the Achilles tendon during a particular activity (such as running) or shortly after. Moderate - the Achilles tendon may swell. In some cases, a hard lump (nodule) may form in the tendon. Severe - any type of activity that involves weight bearing causes pain of the Achilles tendon. Very occasionally, the Achilles tendon may rupture (tear). When an Achilles tendon ruptures, it is said to feel like a hard whack on the heel.
Diagnosis
Examination of the achilles tendon is inspection for muscle atrophy, swelling, asymmetry, joint effusions and erythema. Atrophy is an important clue to the duration of the tendinopathy and it is often present with chronic conditions. Swelling, asymmetry and erythema in pathologic tendons are often observed in the examination. Joint effusions are uncommon with tendinopathy and suggest the possibility of intra-articular pathology. Range of motion testing, strength and flexibility are often limited on the side of the tendinopathy. Palpation tends to elicit well-localized tenderness that is similar in quality and location to the pain experienced during activity. Physical examinations of the Achilles tendon often reveals palpable nodules and thickening. Anatomic deformities, such as forefoot and heel varus and excessive pes planus or foot pronation, should receive special attention. These anatomic deformities are often associated with this problem. In case extra research is wanted, an echography is the first choice of examination when there is a suspicion of tendinosis. Imaging studies are not necessary to diagnose achilles tendonitis, but may be useful with differential diagnosis. Ultrasound is the imaging modality of first choice as it provides a clear indication of tendon width, changes of water content within the tendon and collagen integrity, as well as bursal swelling. MRI may be indicated if diagnosis is unclear or symptoms are atypical. MRI may show increased signal within the Achilles.
Nonsurgical Treatment
In order to treat achilles tendinitis effectively, it is important to complete a thorough examination of the entire lower extremity. Once the true cause is identified, a comprehensive treatment program can be initiated to reduce inflammation and improve any faulty lower extremity biomechanics. Treatment options may include biomechanical analysis of gait. Splinting/bracing to alleviate the strain on the tendon. Soft tissue mobilization/manual therapy to decrease inflammation and promote healing of the tendon. Strengthening/flexibility and proprioceptive exercises. Home exercise program. Modalities for pain and inflammation (i.e. ultrasound, iontophoresis, electrical stimulation, ice). Methods to alter faulty mechanics (i.e taping, orthotics). Education about lifestyle changes (i.e. proper shoes, activity modification).

Surgical Treatment
The type of surgery you will have depends on the type of injury you are faced with. The longer you have waited to have surgery will also be a factor that determines what type of surgery is needed. With acute (recent) tearing the separation in your Achilles tendon is likely to be very minimal. If you have an acute tear you may qualify for less invasive surgery (such as a mini-open procedure). Surgeons will always choose a shorter, less invasive procedure if it is possible to do so. Most surgeons know that a less complicated procedure will have less trauma to the tendon and a much quicker rate of recovery after the surgery.
Prevention
To prevent Achilles tendonitis or tendonosis from recurring after surgical or non-surgical treatment, the foot and ankle surgeon may recommend strengthening and stretching of the calf muscles through daily exercises. Wearing proper shoes for the foot type and activity is also important in preventing recurrence of the condition.